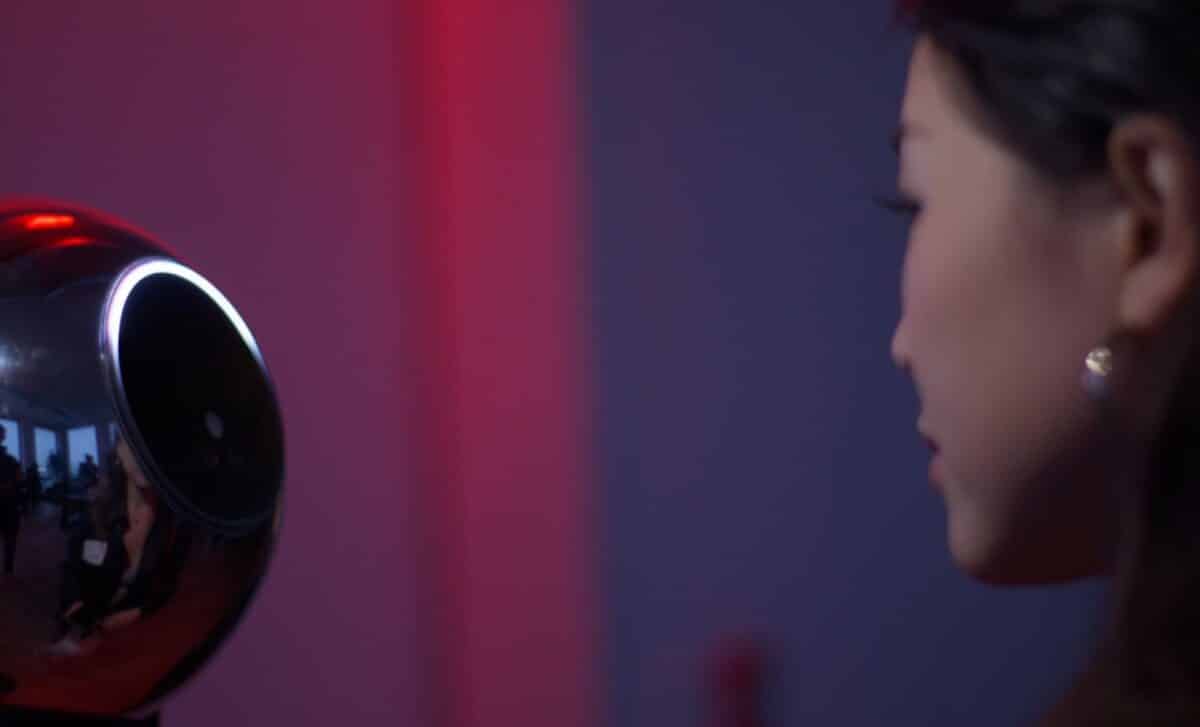
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman has introduced World ID, a biometric digital identity system using iris scans to prove individuals are human online. The project deploys a device called the Orb, which scans the iris and stores an encrypted code on a blockchain platform for secure authentication.
The initiative aims to combat the rise of AI-generated bots by enabling platforms to verify users’ identities without revealing personal data. However, despite its potential benefits, the technology has sparked significant debate around the security and privacy of sensitive biometric information.
How World ID Uses Iris Scanning and Blockchain to Authenticate Users
World ID operates through the Orb, a spherical device that captures a unique iris pattern and converts it into an encrypted IrisCode. This code is stored on a blockchain-based system designed to protect user privacy by allowing identity verification without exposing personal details, according to statements from the project team.
Once individuals complete the iris scan, they receive a World ID credential usable for authentication on platforms that have integrated the protocol. These include major services such as Reddit, Telegram, and Shopify.
To encourage adoption, new users are awarded WLD cryptocurrency tokens equivalent to $40, which can be traded or spent within the network.
The project has already launched in several US cities including Austin, Atlanta, Los Angeles, Nashville, Miami, and San Francisco. It plans to install approximately 7,500 Orb devices nationwide by year-end, targeting up to 180 million users, according to reports.
Privacy and Security Concerns Prompt Global Scrutiny
Despite its ambitious rollout, World ID faces widespread criticism related to the risks of storing biometric data in a centralised database. Privacy advocates and cybersecurity experts warn that linking irreversible biometric identifiers to digital identities could lead to surveillance and misuse.
Several governments, including Spain, Argentina, Kenya, and Hong Kong, have suspended or investigated the project over concerns about excessive data collection and lack of transparency, according to public statements.
Critics have also highlighted the irony of OpenAI’s involvement, as the company’s AI developments contribute to the bot proliferation the system seeks to address.
The irreversible nature of biometric data means that once compromised, it cannot be changed or revoked, raising the stakes for users’ privacy. Regulators continue to debate appropriate safeguards and ethical frameworks to govern the use of such technology.
World ID represents a novel attempt to bridge the gap between advancing artificial intelligence and secure human verification online. While it offers promising tools for combating digital impersonation, the project’s long-term acceptance will depend on addressing profound privacy and security challenges.