The UK’s Individual Savings Accounts (Cash ISAs) are about to undergo a number of changes as part of the Chancellor’s Budget announcement in March. Savers will need to adjust their strategies to make the most of these financial tools.
Starting with the new tax year on 6 April, these changes promise to reshape the way savers use these financial tools. However, let’s find out exactly what these changes mean and how UK consumers can take full advantage of them.
Understanding Cash ISAs
A Cash ISA is a tax-free savings account, explains Katie Brain, consumer banking specialist at Defaqto. It allows customers to deposit money and earn tax-free interest of up to £20,000 per tax year.
Those with reduced rate savings over £19,820 or higher rate savings over £9,920 are likely to benefit from the changes to Cash ISAs. These changes are particularly relevant for the current tax year.
Unlike normal savings accounts, cash ISAs come in different types. With easy access, you can withdraw money whenever you want, and with fixed rate, you get a guaranteed rate, but you’re expected to tie up your money for a set period of time.
Imminent Changes to Cash ISAs
The 25th anniversary of Cash ISAs is coming up in April. It has evolved considerably over the years, from an allowance of just £7,000 in 1999 to £20,000 today. Such changes are set to come into effect on 6 April, following the recent Budget announcement. In particular, this involves :
- Opening Multiple ISAs Within the Same Tax Year: In Katie Brain’s view, perhaps the most significant change is that individuals will now be able to open multiple ISAs of the same type within the same tax year. She says, though, that this is not mandatory and service providers can choose to limit subscriptions to one ISA per tax year.
- Additional Deposits During the Term of Fixed Rate ISAs: A number of providers allow savers to make extra deposits during the term of a fixed rate ISA. Doing so can provide protection against falling interest rates, particularly for fixed-rate ISAs.
- Change to Age Limits for Adult ISAs: Age limits for an adult ISA will increase from 16 to 18. However, 16 and 17-year-olds can still contribute to a Junior ISA, but with a lower tax-free allowance of £9,000 per tax year.
- Partial Transfers Out of Existing ISAs: Retail savers will now be able to transfer a proportion of the existing ISA balance from one provider to another. This could be beneficial if savers wish to secure better rates elsewhere, while retaining some balance in their existing ISA.
To whom are ISAs intended?
Effective from 2016, the Individual Savings Allowance (ISA) means that you receive a tax-free amount of interest…
- Taxpayers on the basic rate of 20% can earn up to £1,000 of interest a year tax-free.
- Higher rate taxpayers (40%) can earn £500 a year tax-free.
- Higher rate taxpayers (45%) are not entitled to PSA.
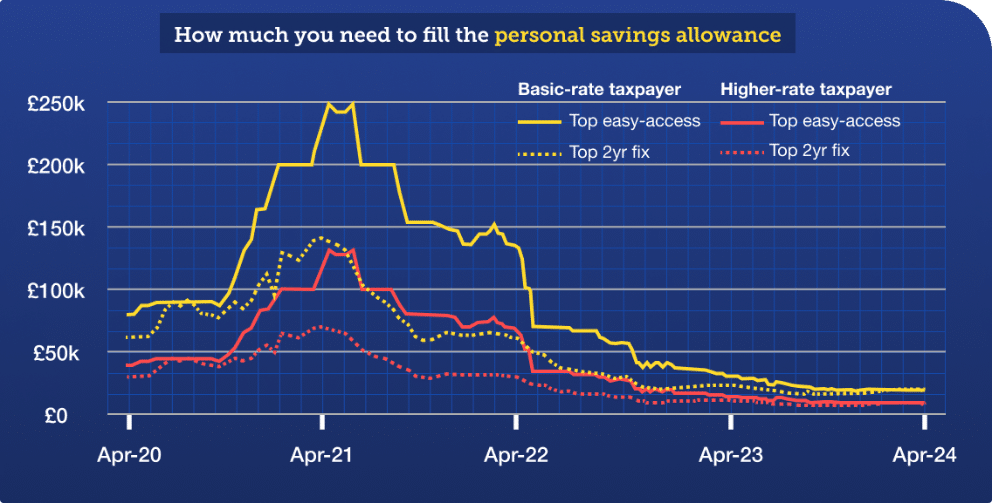
However, keep in mind that these are the interest rates you can earn, so you need a lot of savings to generate them. Plus, as interest rates on savings have been very low between 2016 and 2022, so very few people have paid tax on savings interest. Once, it took around £250,000 of easily accessible higher savings to generate that interest.
Thankfully, with the new coming changes, taxpayers at the basic rate require only around £20,000 of normal savings to pay tax, and higher-rate taxpayers around £10,000…
The Various Types of ISAs
There are many types of ISA available to investors, but Cash ISAs are just one of them. Other types of ISA include
- Lifetime ISA (LISA): Designed for first-time buyers, this type of ISA can also be used for retirement purposes. Individuals can save up to £4,000 per tax year, which the government then tops up by 25%. You can save up to the age of 40.
- Junior ISA (JISA): Parents or guardians can open a JISA on behalf of a child, with an annual allowance of up to £9,000. Contributions can be made by anyone, including grandparents and extended family.
- Stocks and Shares ISA: Allows you to invest in a range of financial products and earn tax-free interest.
- Innovative Finance ISA: This ISA makes it easier to invest in peer-to-peer lending or crowdfunding schemes, while benefiting from the tax-free status of an ISA.









That’s a real good investment need to think about
That’s a good deal you will never go wrong that’s the way especially if you get fixed rates.